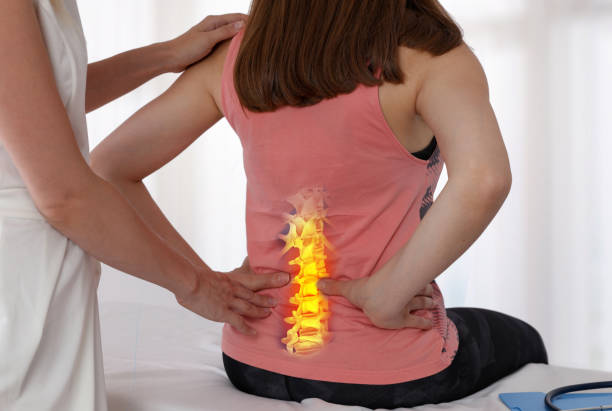
Pain is a universal experience that can range from mild discomfort to debilitating suffering. It can affect physical and emotional well-being, impacting daily activities and quality of life. Understanding pain relief involves knowing the different types of pain, the available relief methods, and the underlying mechanisms at play. This comprehensive guide aims to explore the various facets of pain relief, helping individuals find effective strategies to manage their discomfort.
Types of Pain
1. Acute Pain
Acute pain is typically short-term and results from injury, surgery, or illness. It serves as a warning signal that something is wrong. Common examples include pain from a sprained ankle, a broken bone, or post-surgical discomfort. Acute pain usually resolves as the underlying cause heals.
2. Chronic Pain
Chronic pain persists for longer than three months and can continue even after the initial injury has healed. Conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and chronic back pain fall under this category. Chronic pain can be more challenging to treat and may require a multifaceted approach.
3. Neuropathic Pain
This type of pain arises from damage to the nervous system, often resulting in sensations like burning, tingling, or shooting pain. Conditions such as diabetes (neuropathy), shingles, and multiple sclerosis can lead to neuropathic pain.
Understanding Pain Mechanisms
Pain perception involves a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors. The process includes:
- Transduction: Nerve endings detect harmful stimuli and convert them into electrical signals.
- Transmission: These signals are sent to the spinal cord and then to the brain.
- Perception: The brain interprets the signals as pain.
- Modulation: The body’s natural pain control mechanisms can enhance or diminish pain perception through neurotransmitters and hormones.
Pain Relief Methods
1. Medications
Medications are often the first line of defense against pain. They can be classified into several categories:
- Non-Opioid Analgesics: Over-the-counter options like acetaminophen (Tylenol) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Advil) can relieve mild to moderate pain.
- Opioid Analgesics: Prescription medications like morphine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone are used for severe pain but carry risks of dependence and side effects.
- Adjuvant Medications: Drugs not primarily designed for pain relief, such as antidepressants and anticonvulsants, can also help manage certain types of pain, particularly neuropathic pain.
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy involves exercises and treatments designed to improve mobility, strength, and function. Therapists can create personalized exercise plans that target specific pain areas, helping to alleviate discomfort and prevent future injuries.
3. Complementary Therapies
Many individuals seek alternative therapies to complement traditional pain management:
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body, which may help relieve pain and promote healing.
- Massage Therapy: Massage can reduce muscle tension and improve circulation, providing relief for conditions like chronic back pain and tension headaches.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractors focus on spinal alignment and can help relieve pain, particularly in the back and neck.
4. Mind-Body Techniques
Psychological approaches can play a significant role in managing pain:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps individuals change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to pain, improving coping strategies and emotional responses.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: These practices encourage relaxation and present-moment awareness, helping individuals manage pain and reduce stress.
- Biofeedback: This technique uses sensors to monitor physiological functions, teaching individuals to control responses like heart rate and muscle tension, which can alleviate pain.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting healthy lifestyle choices can significantly impact pain management:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and boost endorphins, which act as natural pain relievers.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods (like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats) can help reduce pain.
- Sleep Hygiene: Quality sleep is essential for pain management. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and creating a restful environment can improve sleep quality.
6. Invasive Procedures
For some individuals, more invasive interventions may be necessary:
- Nerve Blocks: These injections can interrupt pain signals from specific nerves, providing temporary relief.
- Surgery: In cases of severe pain caused by structural problems (like herniated discs or arthritis), surgical options may be considered to relieve pressure and restore function.
Finding the Right Pain Relief Strategy
Finding an effective pain relief strategy often involves a combination of approaches. Here are some tips for developing a personalized plan:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Discuss your pain with a medical professional to identify the underlying cause and explore appropriate treatment options.
- Track Your Pain: Keep a pain diary to monitor pain levels, triggers, and relief methods. This can help you and your healthcare provider find the most effective strategies.
- Be Open to Experimentation: Pain relief is highly individualized. What works for one person may not work for another. Be willing to try different methods and adjust your approach as needed.
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on new treatments and pain management strategies. Research is constantly evolving, and new options may become available.
Conclusion
Understanding pain relief is essential for managing discomfort and improving quality of life. By recognizing the different types of pain, the mechanisms behind pain perception, and the various relief methods available, individuals can take an active role in their pain management. Whether through medication, physical therapy, complementary therapies, or lifestyle modifications, finding the right approach can lead to more effective pain control and a better overall quality of life. Always consult a healthcare provider to tailor a plan that meets your specific needs and circumstances.